Defining the Recommended Gap for an Inflatable Seal
Sealing gap is a major factor in the design of an inflatable product. The gap information listed for each profile in the Pneuma-Seal and Q profile standards sections assume the pressure differential across the seal is 0 psig (0 bar) and the configuration is either radially expanding outward or axially expanding. For inflation inward applications, the gap must be reduced to ensure the seal does not wrinkle. Type 3 or 4 profiles are not recommended for inflation inward applications.
The illustration below describes a typical sealing application and the information required in order to make the right profile choice. As a general rule, inflation pressure (P3) is 15-20 psig (1-1.33 bar) higher than the pressure differential.
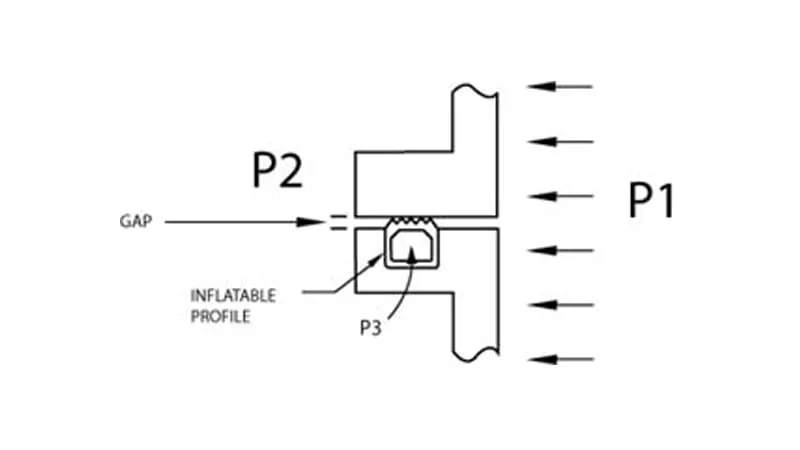
Gap = clearance between deflated seal and opposing surface
P1 = pressure inside the vessel or equipment
P2 = Outside (atmosphere)
P3 = Inflation pressure
Pressure Differential = P1-P2
Example# 1: If P1 = atmosphere and P2 = atmosphere, then the pressure differential across the seal = 0 psig (0 bar). The recommended inflation pressure for the seal would then be 15 psi (1 bar). In this case, we would recommend any of our extruded profiles - most likely a Type 1 profile.
Example# 2: If P1 = 25 psig (~ 2 bar) and P2 = atmosphere, then the pressure differential across the seal = 25 psig (~ 2 bar). Recommended inflation pressure (P3) in this instance would then be 45 psig (~ 3 bar). For this application, we would recommend either a fabric reinforced profile or a high pressure/low gap Type 10 design.
Some general guidelines to consider are:
- For low pressure differentials and small gaps, choose a non-reinforced Type 1 or Type 2 profile.
- For high pressure differentials and small gaps, we recommend a Type 10 profile. For low pressure differentials and large gaps, choose a non-reinforced Type 1 or Type 2 profile.
- For high pressure differentials and large gaps, a fabric reinforced Type 1, Type 2, or Type 3 profile is generally used.
- As a general rule, 0-5 psig (0-0.34 bar) is considered low pressure differential; anything above this would be considered a high pressure differential.
- Where possible, we recommend operating the seal at the minimum required pressure in order to achieve an effective seal. This would increase the seal's longevity and maximize performance.
- Under special circumstances, the maximum operating pressures may be increased if the gap is reduced or the profile is fully contained. If your design requires something unique, please contact us for application assistance.
Please note pressure ratings are guidelines only and may vary depending on the gap to be sealed, safety considerations, etc. If you have any questions, please contact us for application assistance.
Clamping and Actuating Applications
For clamping and actuating applications, the gap has a major influence on the force generated. Typically, the lower the gap, the greater the force generated because overall surface area (or footprint) is maximized. We have some data regarding force for our Pneuma-Cel bladders and can obtain data on other profiles if required.